[목차]
1) 5주차 오늘 배울거
2) 조회한 데이터에 아무 값이 없다면 어떻게 해야할까?
3) 조회한 데이터가 상식적이지 않은 값을 가지고 있다면 어떻게 해야할까?
4) [실습] SQL 로 Pivot Table 만들어보기
5) 업무 시작을 단축시켜 주는 마법의문법 (Window Function - RANK, SUM)
6) 날짜 포맷과 조건까지 SQL 로 한 번에 끝내기 (포맷함수)
*실습
1) 5주차 오늘 배울거
- 예상하지 못한 값이 Query 결과에 나온다면 어떻게 처리해야할까?
- 엑셀에서 해야하는 Pivot, SQL 로 한 번에 구현할 수 있을까?
- SQL 로 이런 것까지 할 수 있다니!
2) 조회한 데이터에 아무 값이 없다면 어떻게 해야할까?
- 있어야할 데이터가 없다면 어떻게 처리해야할까
- 데이터가 없을 때의 연산 결과 변화 케이스
- 테이블에 잘못된 값이 들어있을 수 있다!
- JOIN 을 했을 때 값이 없는 경우도 있었죠!
- 사용할 수 없는 데이터가 들어있거나, 값이 없는 경우네 어떻게 해야할까?
- 데이터가 없을 때의 연산 결과 변화 케이스


- 방법 1 : 없는 값을 제외하기
- Mysql 에서는 사용할수 없는 값일 때 해 당 값을 연산에서 제외한다! -> 0으로간주
- 평균 rating 을 구하는 쿼리를 아래와 같이 작성한다면 실제 연산에 사용되는 데이터는 다음과 같다!
select restaurant_name,
avg(rating) average_of_rating,
avg(if(rating<>'Not given', rating, null)) average_of_rating2
from food_orders
group by 1

- 따라서 명확하게 연산을 지정해주기 위해 null 문법을 이용해야한다!
select a.order_id,
a.customer_id,
a.restaurant_name,
a.price,
b.name,
b.age,
b.gender
from food_orders a left join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.customer_id is not null


- 방법 2 : 다른 값을 대신 사용하기
- 사용할 수 없는 값 대신 다른 값을 대체해서 사용하는 방법이 있다.
- 데이터 분석 시에는 평균값 혹은 중앙값 등 대표값을 이용하여 대체 해주기도 한다.
- 예시 : age 컬럼의 null 을 20으로 대채해서 계산해보자!
select a.order_id,
a.customer_id,
a.restaurant_name,
a.price,
b.name,
b.age,
coalesce(b.age, 20) "null 제거",
b.gender
from food_orders a left join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.age is null

3) 조회한 데이터가 상식적이지 않은 값을 가지고 있다면 어떻게 해야할까?
- 분석을 하다보면 상식적이지 않은 데이터가 나온다면 어떻게 해야할까?
- 케이스1 : 주문고객의 나이 : 음식주문의 고객나이가 상식적이지 않은 값을 가질때!
- 케이스2 : 결제 일자 : 결제의 겨우 최근 일자가 있어야 하는데 비교적 먼 시간때의 결제일이 있을때


- 해결 방법
- 조건문으로 가장 큰 값, 가장 작은 값의 범위를 지정해 줄 수 있다.
- 상식적인 수준 안에서 범위를 지정해 준다 - 위의 나이의 경우 다음과 같이 범위를 설정해 줄 수 있다.
- 조건문으로 가장 큰 값, 가장 작은 값의 범위를 지정해 줄 수 있다.
select customer_id, name, email, gender, age,
case when age<15 then 15
when age>80 then 80
else age end "범위를 지정해준 age"
from customers
4) [실습] SQL 로 Pivot Table 만들어보기
- [실습] 음식점별 시간별 주문건수 Pivot Table 뷰 만들기
(15~20시 사이, 20시 주문건수 기준 내림차순)
음식점별, 시간별 주문건수 집계하기
select a.restaurant_name,
substring(b.time, 1, 2) hh,
count(1) cnt_order
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
where substring(b.time, 1, 2) between 15 and 20
group by 1, 2
pivot view 구조 만들기
select restaurant_name,
max(if(hh='15', cnt_order, 0)) "15",
max(if(hh='16', cnt_order, 0)) "16",
max(if(hh='17', cnt_order, 0)) "17",
max(if(hh='18', cnt_order, 0)) "18",
max(if(hh='19', cnt_order, 0)) "19",
max(if(hh='20', cnt_order, 0)) "20"
from
(
select a.restaurant_name,
substring(b.time, 1, 2) hh,
count(1) cnt_order
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
where substring(b.time, 1, 2) between 15 and 20
group by 1, 2
) a
group by 1
order by 7 desc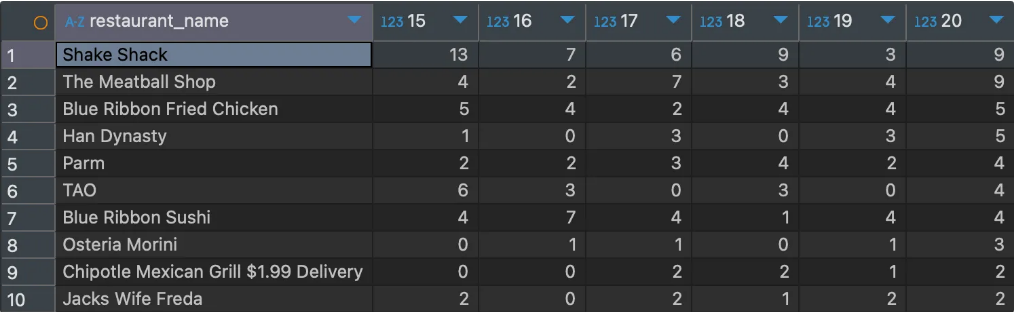
- [실습] 성별, 연령별 주문건수 Pivot Table 뷰 만들기 (나이는 10~59세 사이, 연령 순으로 내림차순)
성별, 연령별 주문건수 집계하기
select b.gender,
case when age between 10 and 19 then 10
when age between 20 and 29 then 20
when age between 30 and 39 then 30
when age between 40 and 49 then 40
when age between 50 and 59 then 50 end age,
count(1)
from food_orders a inner join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.age between 10 and 59
group by 1, 2
Pivot view 구조 만들기
select age,
max(if(gender='male', order_count, 0)) male,
max(if(gender='female', order_count, 0)) female
from
(
select b.gender,
case when age between 10 and 19 then 10
when age between 20 and 29 then 20
when age between 30 and 39 then 30
when age between 40 and 49 then 40
when age between 50 and 59 then 50 end age,
count(1) order_count
from food_orders a inner join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.age between 10 and 59
group by 1, 2
) t
group by 1
order by 1 desc

5) 업무 시작을 단축시켜 주는 마법의문법 (Window Function - RANK, SUM)
- Window Function 의 사례와 기본구조
- Window Function은 각 행의 관계를 정의하기 위한 함수로 그룹 내의 연산을 쉽게 만들어준다.
- 예를 들어
- 한식 식당 중에서 주문건수가 많은 순으로 순위를 매기고 싶은데 가능할까?
- 한식 식당 전체 주문건수 중에서 A 식당이 차지하는 비율을 알고 싶은데 가능할까?
- 2건 이상 주문을 한 소비자 중에, 처음 주문한 식당과 2번째로 주문한 식당을 같이
조회할 수 있을까?
- 기본 SQL 구조로 해결하기 위해서는 복잡한 Subquery 문을 이용하거나, 여러번의 연산을
수행해줘야 하지만, 자체적으로 제공해주는 기능을 이용하면 조금더 편리하다 - 기본 구조
window_function(argument) over (partition by 그룹 기준 컬럼 order by 정렬 기준)
- widon_function : 기능 명을 사용해준다 ( sum, avg 와 같이 기능명이 있다)
- argument : 함수에 따라 작성하거나 생략한다
- partition by : 그룹을나누기 위한 기준이다. group by 절과 유사하다고 생각하면 된다
- order by : window function 을 적용할 때 정렬 할 컬럼 기준을 적어준다
실습 1
- N 번째까지의 대상을 조회하고 싶을때, Rank
- Rank 는 이름에서 유추할 수 있듯이 '특정 기준으로 순위를 매겨주는' 기능이다
- 예를 들어, 주문 건수별 순위 매기기, 결제 시간이 빠른 순으로 순위 매기기 등이 가능하다
- 실습 : 음식 타입별로 주문 건수가 가장 많은 상점 3개씩 조회하기
- 음식 타입별, 음식점 별 주문 건수 집계하기
- Rank 함수 적용하기
- 3위까지 조회하고, 음식 타입별, 순위별로 정렬하기
select cuisine_type, restaurant_name, count(1) order_count
from food_orders
group by 1, 2select cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
rank() over (partition by cuisine_type order by order_count desc) rn,
order_count
from
(
select cuisine_type, restaurant_name, count(1) order_count
from food_orders
group by 1, 2
) a
select cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
order_count,
rn "순위"
from
(
select cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
rank() over (partition by cuisine_type order by order_count desc) rn,
order_count
from
(
select cuisine_type, restaurant_name, count(1) order_count
from food_orders
group by 1, 2
) a
) b
where rn<=3
order by 1, 4
실습 2
- 전체에서 차지하는 비율, 누적합을 구할때, Sum
- Sum 은 앞서 배운 합계를 구하는 기능과 동일하다
- 다만, 누적합이 필요하거나카테고리별 합계컬럼와 원본 컬럼을 함께 이용할 때
유용하게 사용할 수 있다
- 실습 : 각 음식점의 주문건이 해당 음식 타입에서 차지하는 비율을 구하고,
주문건이 낮은 순으로 정령했을 때 누적 합 구하기- 음식 타입별, 음식점별 주문 건수 집계하기
- 카테고리별 합, 카테고리별 누적합 구하기
select cuisine_type, restaurant_name, count(1) order_count
from food_orders
group by 1, 2select cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
cnt_order,
sum(cnt_order) over (partition by cuisine_type) sum_cuisine,
sum(cnt_order) over (partition by cuisine_type order by cnt_order) cum_cuisine
from
(
select cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
count(1) cnt_order
from food_orders
group by 1, 2
) a
order by cuisine_type , cnt_order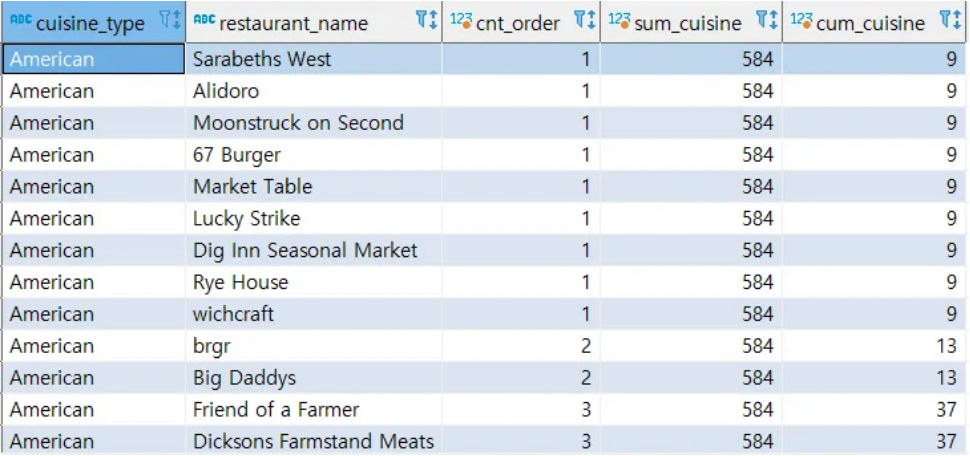
6) 날짜 포맷과 조건까지 SQL 로 한 번에 끝내기 (포맷함수)
- 날짜 데이터 이해
- 날짜 데이터의 여러 포맷
select date(date) date_type,
date
from payments

select date(date) date_type,
date_format(date(date), '%Y') "년",
date_format(date(date), '%m') "월",
date_format(date(date), '%d') "일",
date_format(date(date), '%w') "요일"
from payments
- 실습
- 년도, 월을 포함하여 데이터 가공하기
- 년도, 월별 주문건수 구하기
- 3월 조건으로 지정하고, 년도별로 정렬하기
select date_format(date(date), '%Y') y,
date_format(date(date), '%m') m,
order_id
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_idselect date_format(date(date), '%Y') y,
date_format(date(date), '%m') m,
count(1) order_count
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
group by 1, 2select date_format(date(date), '%Y') "년",
date_format(date(date), '%m') "월",
date_format(date(data), 'Y%m') "년월",
count(1) "주문건수"
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
where date_format(date(date), '%m')='03'
group by 1, 2
order by 1
*실습
- 음식 타입별, 연령별 주문건수 pivot view 만들기
select cuisine_type,
max(if(age=10, order_count, 0)) "10대",
max(if(age=20, order_count, 0)) "20대",
max(if(age=30, order_count, 0)) "30대",
max(if(age=40, order_count, 0)) "40대",
max(if(age=50, order_count, 0)) "50대"
from
(
select a.cuisine_type,
case when age between 10 and 19 then 10
when age between 20 and 29 then 20
when age between 30 and 39 then 30
when age between 40 and 49 then 40
when age between 50 and 59 then 50 end age,
count(1) order_count
from food_orders a inner join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where age between 10 and 59
group by 1, 2
) t
group by 1
'부트캠프' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 웹 개발 강의 정리 2 (0) | 2025.03.21 |
|---|---|
| 웹개발 강의 정리 1 (0) | 2025.03.21 |
| SQL 오늘 배운 강의 정리 4 (0) | 2025.03.19 |
| SQL 오늘 강의 내용 정리 3 (0) | 2025.03.19 |
| SQL 오늘 강의 내용 정리 2 (0) | 2025.03.18 |